Lesson 5: Reindeer Boots Key Stage 2 & Key Stage 2: History
Investigating clothing worn by polar explorers on Scott's expeditions
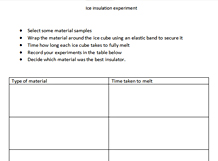
Designing suitable footwear.
Early Antarctic explorers used knowledge from indigenous people who live in the Circumpolar North, in the Arctic Circle, to help them understand how to create suitable footwear for them to wear in Antarctica.
George Murray Levick, the surgeon on the Terra Nova Expedition, had boot covers made for him by local people in the northern Arctic and they were the type of footwear that these people wore themselves.
Download lesson plan:
Purpose of study:
History - Know and understand how people's lives have shaped this nation and how Britain has influenced and been influenced by the wider world.
Understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed.
Science - They should ask their own questions about what they observe and make some decisions about which types of scientific enquiry are likely to be the best ways of answering them, including observing changes over time, noticing patterns, grouping and classifying things, carrying out simple comparative and fair tests and finding things out using secondary sources of information. They should draw simple conclusions and use some scientific language, first, to talk about and, later, to write about what they have found out.
| National Curriculum Aims / Attainment Targets | Activity focus |
|---|---|
History:
Science:
|
|
Science:
|
|
Science:Working scientifically
States of matter
|
|